Google Tag Manager vs Google Analytics: Key Differences (2025)
Two of Google’s most powerful tools for website tracking and analytics often get confused or used interchangeably. While Google Tag Manager (GTM) and Google Analytics (GA) work beautifully together, they serve completely different purposes in your digital marketing stack.
Understanding the distinction between these platforms can transform how you collect data, track user behavior, and make informed business decisions. Whether you’re a marketing professional trying to streamline your tracking setup or a business owner looking to better understand your website performance, knowing when and how to use each tool is essential.
This guide breaks down the core differences between Google Tag Manager and Google Analytics, explores how they complement each other, and helps you determine which approach works best for your specific needs.
What is Google Tag Manager?
Google Tag Manager is a free tag management system that allows you to deploy and manage marketing tags on your website without modifying code directly. Think of it as a container that holds all your tracking codes, pixels, and scripts in one centralized location.
Instead of asking developers to add tracking codes for every new campaign or tool you want to implement, GTM provides a user-friendly interface where marketers can add, edit, and remove tags themselves. This includes tracking codes for Google Analytics, Facebook Pixel, Google Ads conversion tracking, heat mapping tools, and countless other third-party services.
The platform uses triggers (conditions that determine when tags fire) and variables (dynamic values that tags can reference) to ensure your tracking codes activate at precisely the right moments. For example, you might set up a trigger to fire a conversion tracking tag only when users reach your thank-you page after making a purchase.
What is Google Analytics?
Google Analytics is a web analytics platform that collects, processes, and reports data about your website visitors and their behavior. It’s the tool that actually captures information about how users interact with your site and presents it in an organized, actionable format.
GA tracks metrics like page views, session duration, bounce rate, conversion rates, and user demographics. It shows you which pages perform best, where your traffic comes from, and how visitors move through your site. The platform also offers advanced features like audience segmentation, goal tracking, and e-commerce reporting.
While Google Analytics focuses on data collection and reporting, it doesn’t manage the deployment of tracking codes across your website. This is where the confusion between GTM vs GA often arises.
Google Tag Manager vs Google Analytics: Core Differences
Purpose and Function
The fundamental difference lies in what each platform accomplishes. Google Analytics is your data collection and reporting engine, while Google Tag Manager is your tag deployment and management system.
Google Analytics answers questions like “How many visitors did I have last month?” and “Which marketing channels drive the most conversions?” Google Tag Manager handles the technical side of ensuring those data points get captured correctly across your entire website.
User Interface and Complexity
Google Analytics presents data through dashboards, reports, and customizable views designed for analysis and decision-making. The interface focuses on charts, graphs, and data tables that help you understand user behavior patterns.
Google Tag Manager features a more technical interface centered around tags, triggers, and variables. While it’s designed to be user-friendly for marketers, it requires understanding concepts like event tracking and conditional logic.
Data Collection vs Data Management
Google Analytics collects first-party data about your website visitors and stores it for analysis. It creates user sessions, tracks conversions, and builds audience profiles based on behavior.
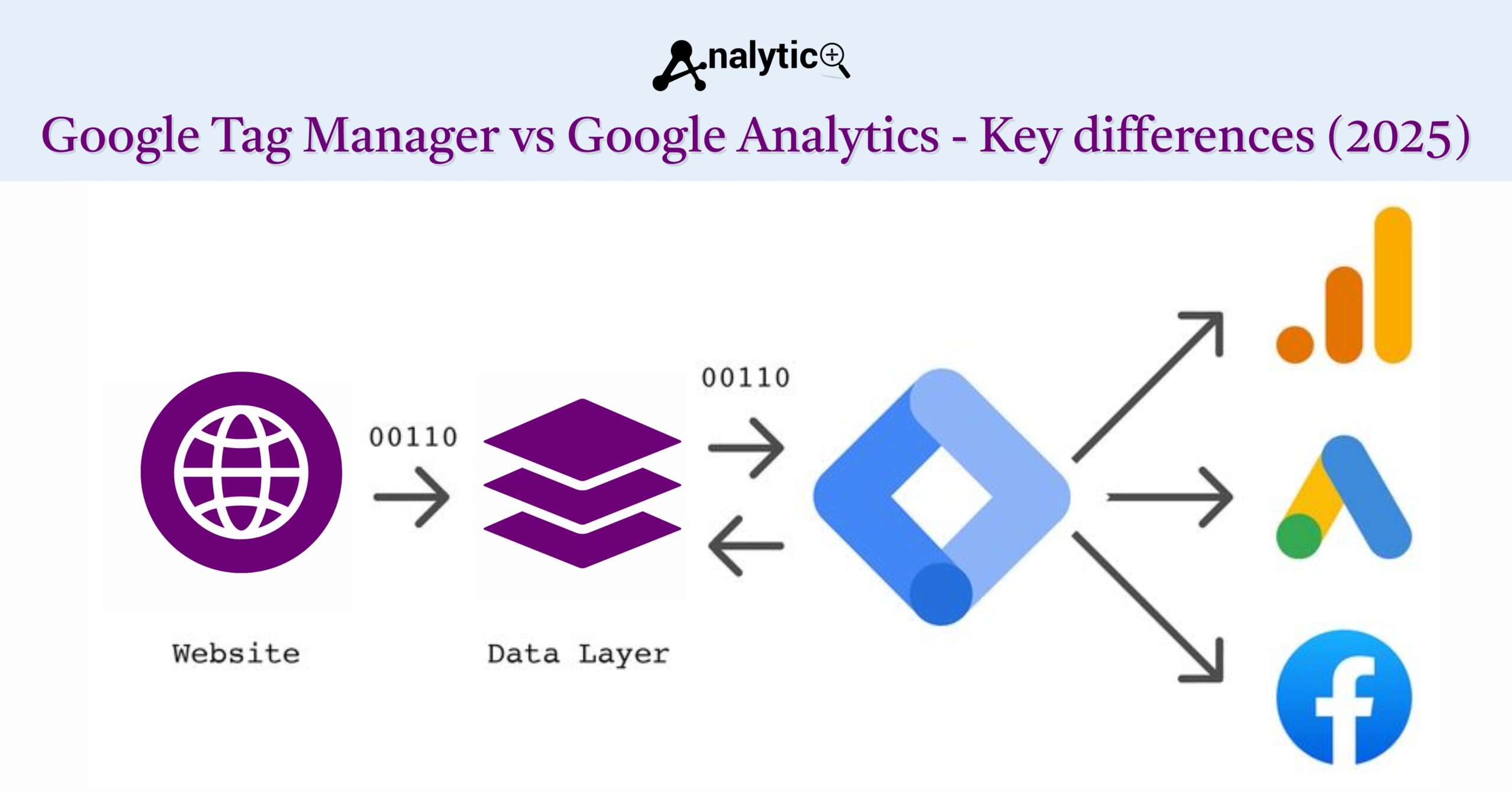
Google Tag Manager doesn’t collect or store data itself. Instead, it manages when and how other tools (including Google Analytics) collect data from your website. It’s essentially a traffic controller for all your tracking implementations.
Implementation Requirements
Implementing Google Analytics traditionally requires adding tracking code to every page of your website. Any changes to tracking setup typically require developer assistance and code modifications.
Google Tag Manager requires only one piece of code installed on your website. Once implemented, marketers can add, modify, or remove tracking for various tools without touching website code again.
How Google Tag Manager and Google Analytics Work Together
Rather than competing platforms, Google Tag Manager and Google Analytics form a powerful partnership. Most websites benefit from using both tools together.
GTM serves as the delivery mechanism for your Google Analytics tracking code. Instead of hard-coding the GA tracking script into your website, you deploy it through Google Tag Manager. This setup provides several advantages.
You can easily modify your Google Analytics configuration without developer involvement. Want to start tracking specific button clicks as events? Set up the tracking entirely within GTM. Need to exclude internal traffic from your reports? Configure the filter through your tag management setup.
The combination also enables more sophisticated tracking implementations. You can set up enhanced e-commerce tracking, cross-domain measurement, or custom event tracking with greater flexibility than traditional GA implementations allow.
Additionally, using GTM with GA makes it easier to implement tracking for multiple Google Analytics properties simultaneously. You might track data for your main GA4 property while also sending information to a separate Universal Analytics property during migration periods.
Google Tag Manager Alternatives and Comparisons
While Google Tag Manager dominates the tag management space, several alternatives exist for organizations with specific needs.
Adobe Experience Platform Launch offers enterprise-level tag management with advanced workflow controls and approval processes. Tealium iQ provides similar functionality with additional data privacy and governance features.
For organizations concerned about data privacy or third-party dependencies, server-side tag management solutions like Google’s own Server-side GTM or custom implementations provide more control over data collection.
However, for most websites, Google Tag Manager’s combination of functionality, ease of use, and cost (free) makes it the clear choice for tag management needs.
Google Analytics vs Google Search Console
It’s worth noting that Google Search Console serves a different purpose entirely from both Google Tag Manager and Google Analytics. While GA focuses on user behavior and website performance, Search Console provides insights specifically about your site’s presence in Google search results.
Search Console shows which search queries bring users to your site, identifies technical SEO issues, and provides data about your search performance. Many websites use Google Analytics, Google Tag Manager, and Google Search Console together for comprehensive digital marketing insights.
Choosing the Right Setup for Your Website
For most websites, implementing both Google Tag Manager and Google Analytics provides the best solution. This approach offers maximum flexibility for current tracking needs while providing a foundation for future requirements.
Start with Google Tag Manager if you’re building a new website or planning to implement multiple tracking tools. Deploy your Google Analytics tracking through GTM rather than hard-coding it directly.
If you already have Google Analytics implemented directly on your site, consider migrating to a GTM-based setup during your next website update or when you need to add additional tracking tools.
Small websites with minimal tracking requirements might function adequately with just Google Analytics implemented directly. However, the benefits of tag management become apparent quickly as your tracking needs grow.
Maximizing Your Analytics and Tag Management Strategy
The combination of Google Tag Manager and Google Analytics opens up powerful possibilities for data collection and analysis. By understanding how these tools complement each other rather than compete, you can build a more sophisticated and flexible tracking infrastructure.
Start by implementing Google Tag Manager on your website if you haven’t already. Then deploy your Google Analytics tracking through GTM to begin experiencing the benefits of centralized tag management. As your tracking needs evolve, you’ll appreciate the flexibility this foundation provides.
Remember that both tools require ongoing maintenance and optimization. Regular audits of your tag setup and analytics configuration ensure you’re collecting accurate data and making informed decisions based on reliable insights.

