Server-Side vs Client-Side Tagging: Your 2025 Guide
Server-side tagging vs client-side tagging, Web tracking has evolved dramatically over the past few years. Privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA, combined with the deprecation of third-party cookies, have forced marketers and developers to rethink their tagging strategies. The question many teams face now isn’t whether to implement tracking, but how to do it effectively while respecting user privacy.
Two approaches dominate the conversation: server-side tagging and client-side tagging. Each method offers distinct advantages and challenges, and the choice between them can significantly impact your data quality, website performance, and privacy compliance.
This guide breaks down everything you need to know about both approaches, helping you make an informed decision for your organization’s tracking needs in 2025.
Understanding Client-Side Tagging
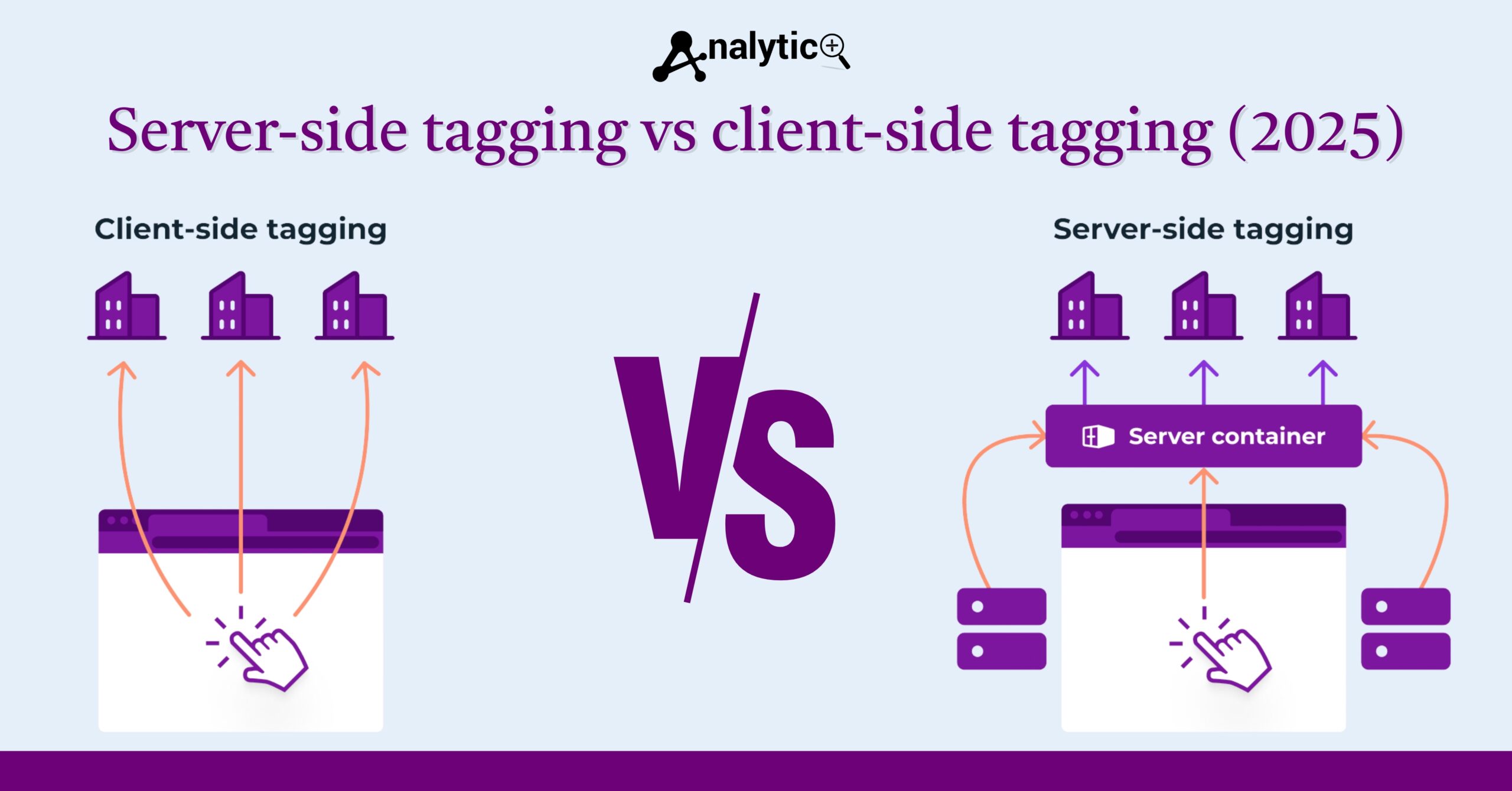
Client-side tagging has been the standard approach for web tracking for over a decade. With this method, tracking codes execute directly in the user’s browser, collecting data and sending it to various analytics platforms and marketing tools.
When a user visits your website, JavaScript tags fire in their browser, gathering information about their behavior, device, and interactions. This data then travels directly from the user’s browser to your analytics platforms like Google Analytics, Facebook Pixel, or other third-party services.
How Client-Side Tagging Works
The process is relatively straightforward. You embed tracking scripts directly into your website’s HTML or manage them through a tag management system like Google Tag Manager. When pages load, these scripts execute, collecting data points such as page views, clicks, form submissions, and scroll depth.
Popular client-side tracking implementations include the standard Google Analytics tracking code, Facebook Pixel, and various marketing automation scripts. Most businesses start with client-side tagging because it requires minimal technical setup and provides immediate access to user data.
Benefits of Client-Side Tagging
Client-side tagging offers several compelling advantages. Setup is typically quick and doesn’t require server infrastructure, making it accessible for businesses of all sizes. The approach provides rich user context, capturing detailed information about browser capabilities, screen resolution, and user interactions that might be difficult to collect server-side.
For many marketing teams, client-side tagging feels more straightforward. You can implement tracking codes directly through platforms like Google Tag Manager without involving your development team extensively. Real-time debugging is also easier since you can inspect network requests and see exactly what data is being sent from the browser.
Limitations of Client-Side Tagging
However, client-side tagging faces significant challenges in 2025. Ad blockers increasingly prevent client-side scripts from executing, leading to substantial data loss. Studies suggest that ad blockers now affect 25-30% of web traffic, creating blind spots in your analytics.
Privacy regulations add another layer of complexity. Client-side tags often struggle with consent management, and the impending deprecation of third-party cookies will limit cross-domain tracking capabilities. Page load speed can also suffer when multiple client-side scripts compete for browser resources.
Browser restrictions continue to tighten, with Safari’s Intelligent Tracking Prevention and Chrome’s Privacy Sandbox initiative limiting how long client-side tracking can persist and what data it can collect.
Exploring Server-Side Tagging
Server-side tagging fundamentals represent a shift in how we approach web tracking. Instead of relying on the user’s browser to execute tracking code, server-side tagging processes data on your own servers before sending it to analytics platforms.
When a user interacts with your website, basic information travels to your server. Your server then processes this data, enriches it with additional context, and forwards it to your chosen analytics and marketing platforms. This approach gives you greater control over what data is collected and how it’s processed.
The Server-Side Tagging Process
Google Tag Manager server-side implementation provides one of the most accessible entry points for server-side tagging. You deploy a server container that acts as a proxy between your website and your analytics platforms. User interactions first hit your server, where tags process the data before sending it downstream.
This architecture allows you to validate, filter, and enhance data before it reaches platforms like Google Analytics or Facebook. You can also implement custom business logic, merge data from multiple sources, and ensure consistent data formatting across all your marketing tools.
Advantages of Server-Side Tagging
Server-side tagging offers compelling benefits for data quality and privacy compliance. Since tracking occurs on your servers, ad blockers cannot interfere with data collection. This typically results in 15-30% more complete data compared to client-side implementations.
Privacy compliance becomes more manageable with server-side tagging. You control exactly what data gets shared with third-party platforms, making it easier to respect user consent preferences and comply with regulations like GDPR. Data security also improves since sensitive information never leaves your controlled environment.
Performance benefits are notable too. Moving tracking logic off the client reduces the JavaScript burden on user browsers, potentially improving page load speeds and user experience. You can also implement more sophisticated data processing without affecting frontend performance.
Server-Side Tagging Challenges
Server-side tagging requires more technical expertise and infrastructure management. You need to maintain servers, monitor uptime, and handle scaling as your traffic grows. Google Tag Manager server-side pricing can also add operational costs, especially for high-traffic websites.
Some data points that are readily available client-side become more challenging to collect server-side. Browser-specific information, real-time user interactions, and certain engagement metrics may require additional implementation work. The setup process is also more complex, often requiring coordination between marketing and development teams.
Server-Side vs Client-Side: Key Comparisons
Data Quality and Completeness
GA4 server-side tracking typically provides more complete data than client-side implementations. While client-side tracking suffers from ad blocker interference, server-side approaches capture nearly all user interactions. However, client-side tracking can access richer contextual data about the user’s browser and device.
Privacy and Compliance
Server-side tagging offers superior privacy controls. You can anonymize data, respect user preferences more granularly, and limit what information third-party platforms receive. Client-side tagging makes privacy compliance more challenging since third-party scripts often collect data beyond your direct control.
Performance Impact
Client-side tags can slow down your website, especially when loading multiple third-party scripts. Server-side tagging reduces this frontend burden, though it shifts the performance consideration to your server infrastructure. The user experience generally improves with server-side implementations.
Implementation Complexity
Client-side tagging wins on simplicity. Most marketers can implement basic client-side tracking without extensive technical knowledge. Server-side tagging requires more planning, technical expertise, and ongoing maintenance, making it better suited for organizations with dedicated technical resources.
Cost Considerations
Client-side tagging has minimal direct costs but may result in data loss that impacts your marketing effectiveness. Server-side tagging involves infrastructure costs and potentially higher tag management expenses, but the improved data quality often justifies the investment.
Choosing the Right Approach for 2025
Your choice between server-side and client-side tagging should align with your organization’s priorities, technical capabilities, and compliance requirements.
Consider server-side tagging if data accuracy is critical to your business, you have strict privacy compliance requirements, or you’re experiencing significant data loss from ad blockers. Organizations with technical resources and higher traffic volumes typically see the greatest benefit from server-side implementations.
Client-side tagging remains viable if you need quick implementation, have limited technical resources, or require access to rich browser-context data that’s difficult to replicate server-side. Many smaller businesses and those just starting with analytics find client-side approaches more accessible.
A hybrid approach often provides the best of both worlds. You can implement server-side tagging for core analytics while maintaining some client-side tags for specific use cases that require browser context or real-time interaction data.
Making the Transition Work
Moving from client-side to server-side tagging requires careful planning. Start by auditing your current tracking implementation to understand what data you’re collecting and which platforms you’re feeding. Prioritize your most critical tracking needs and plan a phased migration.
Test thoroughly before going live with server-side implementations. Data discrepancies between client-side and server-side approaches are common during transitions, so allow time for troubleshooting and optimization. Monitor your analytics closely during the first few weeks after implementation.
Consider working with experienced developers or analytics consultants if your team lacks server-side expertise. The initial investment in professional guidance often pays for itself through faster implementation and fewer data quality issues.
Your Next Steps for Better Web Tracking
The tracking landscape will continue evolving throughout 2025, with privacy regulations becoming stricter and browser restrictions expanding. Organizations that proactively address these changes through thoughtful tagging strategies will maintain competitive advantages in data-driven marketing.
Evaluate your current tracking setup against your business goals and technical capabilities. If data quality issues are impacting your marketing decisions or privacy compliance is becoming burdensome, server-side tagging deserves serious consideration.
Start small with a pilot implementation on a subset of your tracking needs. This approach allows you to build expertise and prove value before committing to a full migration. Remember that the best tagging strategy is one that delivers reliable data while respecting user privacy and maintaining website performance.

